

General consideration IV

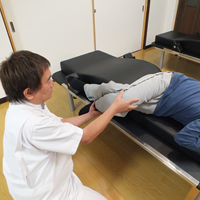
- Symptom
- This problem is shin splints syndrome, which is categorized into: 1. posterior tibial shin splint, 2. tibial periostitis, 3. anterior compartment syndrome, and 4. tibial fracture. These problems are often found with track athletes, basketball players, tennis players, soccer players, and players of other athletic events that involve sprinting.
- Tamatare Remedy
- Tamatare Remedy aligns motor axes of four joints—the talocrural joint, lower ankle bone joint, transverse tarsal joint, and tarsometatarsal joints—with the motor axes of related muscles such as the posterior tibial muscle, anterior tibial muscle, gastrocnemius muscle, soleus muscle, plantaris muscle, long peroneal muscle, and short peroneal muscle. Tamatare Remedy also recovers the metabolism efficiency of these muscles to restore the spring property of the ankle. These treatments cure 1. the posterior tibial shin splint and 2. tibial periostitis.
For a tibial fracture, Tamatare Remedy recovers the metabolism of not only the lower thigh but also of the lower limb skeletal muscles to realize early recovery of motor function. For anterior compartment syndrome (3), we cannot determine here whether the affected athlete will return to play.
- Details
- To run fast, the athlete has to stomp strongly on the ground or floor. The leg motion is repetition of strong dorsal flexion and plantar flexion. The muscles that effect dorsal flexion in this motion are mainly the posterior tibial muscle and the anterior tibial muscle. When these muscle functions deteriorate, the posterior tibial shin splint happens. The tibial periostitis (2) happens when the posterior tibial shin splint (1) further deteriorates. When the bone condition becomes dangerous, the periosteal nerve signals a pain on behalf of the bone. In other words, the periostea plays the role of a stress sensor for the bone. Anterior compartment syndrome (3) indicates an ischemia in the tibial artery, which may cause necrosis of a muscle or a bone, and therefore, is very dangerous. A tibial fracture (4) is a fatigue fracture that happens when the posterior tibial muscle has received a transient or continuous force that exceeds its supporting capacity. A fracture incurred by an accident is not a shin splint. A shin splint does not happen suddenly. It is usually preceded by a pain in the ankle or a side of the foot. The ankle includes a tissue called "retinacula of extensor muscles", which is a tissue denatured from fascia. There will be pain in this tissue or the peroneus, which coordinates ankle movement, before shin splint happens.
A sports injury often develops to a secondary or a tertiary injury, and further into a combined disorder. One should take the first pain as an alarm from the muscle and should prevent a combined injury. The shin splint is a typical injury of such nature.

General consideration III







